Diffusion and osmosis (English Language)
osmosis
The osmosis of (Osmosis) is the movement of solvent. (Often referred to water) through a membrane from a solution of low concentration to high concentration solution (remember a little water and too much water through the membrane, such as membrane Or paper cellos defenseman that we used in our experiments).
The osmosis of (Osmosis) is the movement of solvent. (Often referred to water) through a membrane from a solution of low concentration to high concentration solution (remember a little water and too much water through the membrane, such as membrane Or paper cellos defenseman that we used in our experiments).
**** show osmosis. The water moves very little water through the membrane. (semipermeable membrane) ****.
The osmosis pressure in two related species .
- Osmotic pressure (Osmotic pressure) is the pressure to resist the movement of a solvent through a membrane . Such as cell membranes.
( Osmotic pressure is the force that resists the motion of the water, the water moves from an area with a lot of water to an area with less water resistance , so if there is not much water movement . Water moves through the membrane significantly. ( Not much resistance = low osmotic pressure ) and osmotic water pressure low ).
- Firm pressure (turgor pressure) is the pressure inside the cell. Occurs due to osmosis , water enters the cell and push the cells to swell up or tune . When too much water into the cell if the cell may rupture . If a plant cell is usually due to the rupture of the cell wall, the cell shape .
The balance point of the spread . Osmotic pressure of solution = peak pressure up
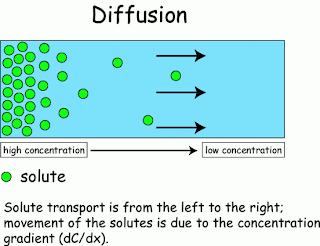
Diffusion
Is the movement of particles from a substance to an area of high density material with low density . By the kinetic energy of the substance itself. ( I had exams Ent ) .
(key word is little substance to substance . Or areas where the substance will move to areas with less substance ) by the spread of the two types .
1.1) over conventional (Simple diffusion) is not broadcasting live carrier . Or help transport (carrier) Nothing like the spread of powdered potassium permanganate in water until the water is colored magenta and around the container . The powder scent or perfume smell
Figure 1 shows a simple diffusion (the substance to substance less).
Figure 2 shows the distribution of gas in the lungs.
.2) diffusion ° Si Tate (Facilitated diffusion) the diffusion of water through a protein carrier (Carrier) embedded in the cell membrane directly to a protein carrier (carrier) is acting like a gate to get molecules into . and out of cells. Diffusion is faster than the diffusion rate of diffusion very simple example, the liver cells and endocytosis . Intestinal epithelial cells . This diffusion occurs in the cells of organisms only.
Figure 3 shows the diffusion ° Si Tate (less substance to substance but must have taken).